
Push Push an image or a repository to a registry Pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry Port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container
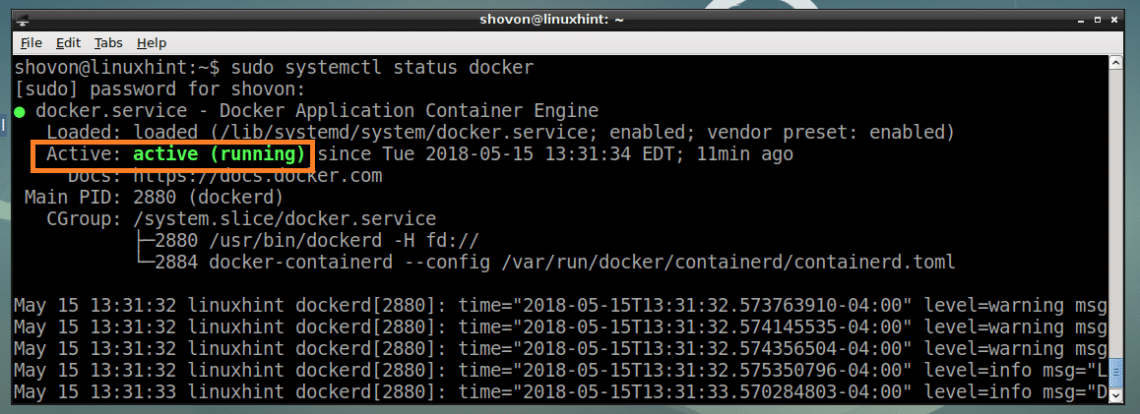
Pause Pause all processes within one or more containers Load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN

Inspect Return low-level information on Docker objects Import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image Outputattach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running containerĬommit Create a new image from a container's changesĬp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystemĭiff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystemĮvents Get real time events from the serverĮxec Run a command in a running containerĮxport Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive You’ll see output like this, although the version number for Docker may be different: Make sure you are about to install from the Docker repo instead of the default Debian repo: Next, update the package database with the Docker packages from the newly added repo: sudo add-apt-repository "deb $(lsb_release -cs ) stable".
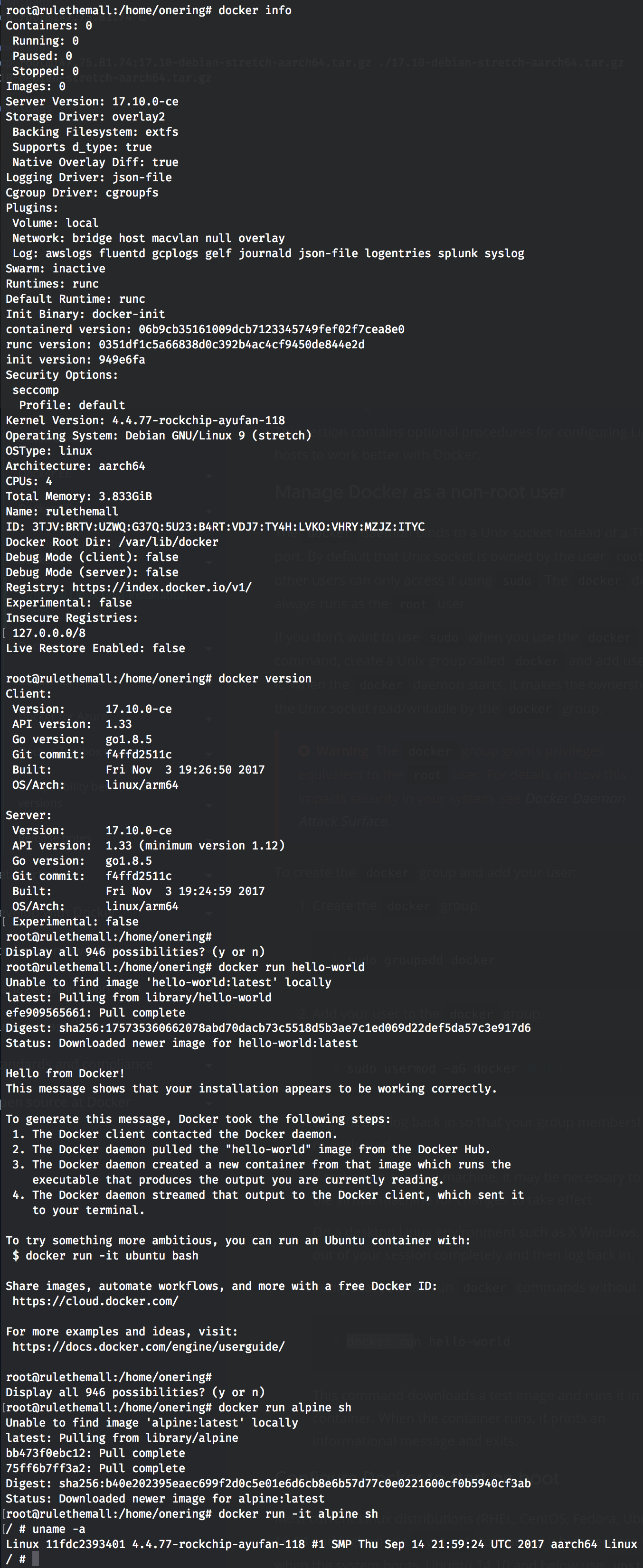
Then add the GPG key for the official Docker repository to your system:Īdd the Docker repository to APT sources:
They’re similar to virtual machines, but containers are more portable, more resource-friendly, and more dependent on the host operating system.įor a detailed introduction to the different components of a Docker container, check out The Docker Ecosystem: An Introduction to Common Components. Containers let you run your applications in resource-isolated processes. Docker is an application that simplifies the process of managing application processes in containers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
